
While our customers are wholesalers, Packard knows that you, the contractor, have a choice. You are often presented with many buying options, and being well-informed about your purchase can help make your job easier and more successful. Our Tech Tips are also very helpful for our wholesalers as we present product information that can help as contractors have questions.
This is why we have dedicated a section of our site for contractors and wholesalers. In this section, you will find helpful product tips, tools and some clips from our training classes. We’ve also provided a distributor locator so you can find the nearest wholesaler who can give you access to Packard products.
I’ve heard that there is a way to measure the actual capacitance provided to a motor while it’s operating. How?
The actual capacitance that a capacitor is providing to an operating motor can be calculated. This is done while the motor is energized. In order to get accurate measurements all doors, panels, filters, and guards must be in place. The coils should be clean and free of obstruction. These conditions are necessary in order to assure that the motor is loaded properly. The load can be greatly impacted by increases and decreases in static pressure, in which case the motor may operate abnormally.
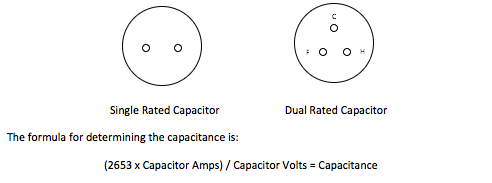
You may have seen this formula with a number different than the 2653. That could occur depending upon how many decimal places the mathematical Pi (3.1415927), which is used to determine the “constant”, is carried out.
To determine the value of Capacitor Amps, using an ammeter, measure the amps on one of the capacitor leads of a single rated capacitor. If a dual rated capacitor, measure the capacitor lead on the hermetic (H) lead for a compressor and the capacitor lead on the fan (F) for a condenser fan motor.
To determine the value for Capacitor Volts, using a multi-meter set on AC volts, measure between the two capacitor terminals on a single rated capacitor. On a dual rated capacitor measure between the common (C) and H terminals for the compressor, and between the C and F terminals for the condenser fan motor.
When applying these values into the formula, the result can be compared to the measured value of the capacitor. The measured value of the capacitor should not be more than +/- 10% of the nameplate rating of the capacitor. If it is, the capacitor should be replaced. If the calculated capacitance differs from the measured value of the capacitor, operating conditions may be affecting the load on the motor. It is very common to measure higher capacitor volts than what the motor is designed for. This can be a result of high static pressure, which reduces load on the motor, resulting in the motor being underloaded. This can lead to premature failure of the capacitor and the motor.
Remember, this formula is only useful when the measurements are accurate. They are only accurate when all of the components of the system are in place and the coils are clean and free of obstructions. It can then provide insight into whether there may be issues with the load on the motor, which can often be associated with static pressure.



Leave a comment